Traditional Insurance Isn't Built For
Today’s Cyber Risks
Our Approach
We combine smart insurance with innovative cybersecurity to help businesses stay ahead of digital threats. Our approach is simple, effective, and designed to keep you confident in a world of constant change. Let us be the partner that secures your future, so you can focus on what you do best.

We are MODERN, We are HERE!
All in one
Corporate Cyber Insurance
External entities, vital for business growth & operational efficiency, can also pose diverse cyber risks to your organisation.
- What's Included
- Not Included
Reputation Damage
Breach response experts will contain the cyber incident & re-secure your network if needed.
Hacker Damages
Costs to repair, replace, or restore websites or electronic data.
Insider Threats
Damages from malicious acts by an employee to yours or vendor’s system.
Loss of Business
Lost profits if a cyber incident interrupts your business operations.
Breach Response by the Hackbusters
Expert help to contain the cyber incident & re-secure your network if needed.
Cyber Deception & Engineering
Money wrongly transmitted or paid to a third-party from a deception scheme, also known as social engineering.
Legal & Regulatory Costs
Legal expense due to regulatory fines or requirements to notify customers.
Third Party Liability
Costs associated with claims against you for a breach of any privacy law with respect to protection of third-party data.
Coverage For Trading Losses
Losses related to trading activities are not covered.
Losses Incurred In Crypto-Currency
Costs associated with crypto-currency losses are excluded.
Use Of Restricted Websites
Damages resulting from the use of restricted or illegal websites are not included.
Cost Of Upgrading Devices
Expenses related to upgrading or improving devices are not covered.
No Coverage for Bodily Injury
No cover for body injury arising out of cyber attacks
No Coverage for Property Damage
No cover for property damage arising out of cyber attacks
Disclaimer: Explanations in "What's Included" are illustrative and subject to the Policy's terms, conditions, and exclusions. Refer to the Policy Document for details.
Cyber Insurance Coverage Report
This report details coverage for cyber-related risks, such as crisis management, data restoration, regulatory penalties, and ransomware. It includes protections for privacy, intellectual property, and corporate security, with exclusions for employer claims, infrastructure failures, and certain contractual obligations.

Reasons Why Mitigata
Is A Better Choice
Real Protection for Real Threats
Traditional insurance isn’t enough for today’s cyber risks. Mitigata’s cyber insurance is built specifically to cover digital threats like hacking, data leaks, and scams that can damage your business.
Quick Help When You Need It Most
If a cyber attack happens, every minute counts. Mitigata’s response team is ready to jump in right away to limit damage, secure your systems, and get you back on track fast.
Covers Financial Losses and Reputation Damage
Cyber incidents can hurt your reputation and cost you money. Mitigata’s coverage protects you from these losses, including lost revenue, legal fees, and any costs tied to regaining customer trust.
Simple, Straightforward Claims Process
Filing claims can be a headache, but Mitigata’s team makes it easy and fast. They handle the tough parts so you can focus on running your business.
All-in-One Cybersecurity Tool
The Mitigata Console is more than insurance—it’s an extra shield for your business. It helps spot weak spots in your systems and works to keep hackers out.
Clarity and Honesty in Coverage
With Mitigata, there are no surprises. Policies are clear about what’s covered and what’s not, so you know exactly what to expect if something goes wrong.
Support Beyond Insurance
Mitigata isn’t just an insurance provider; they’re a partner. They help you understand risks and put strong defenses in place to keep your business safe from cyber threats.
Mitigata Console: Your Cyber Guardian
Mitigata Console isn't just cybersecurity software; it's your digital stronghold against threats. Empowering businesses with proactive defence, it's your vigilant protector of valuable assets. Revolutionising cybersecurity management, it identifies vulnerabilities and defends against breaches, ensuring proactive defence. With Mitigata Console, fortify your defences with confidence, securing infrastructure and upholding trust in digital operations.
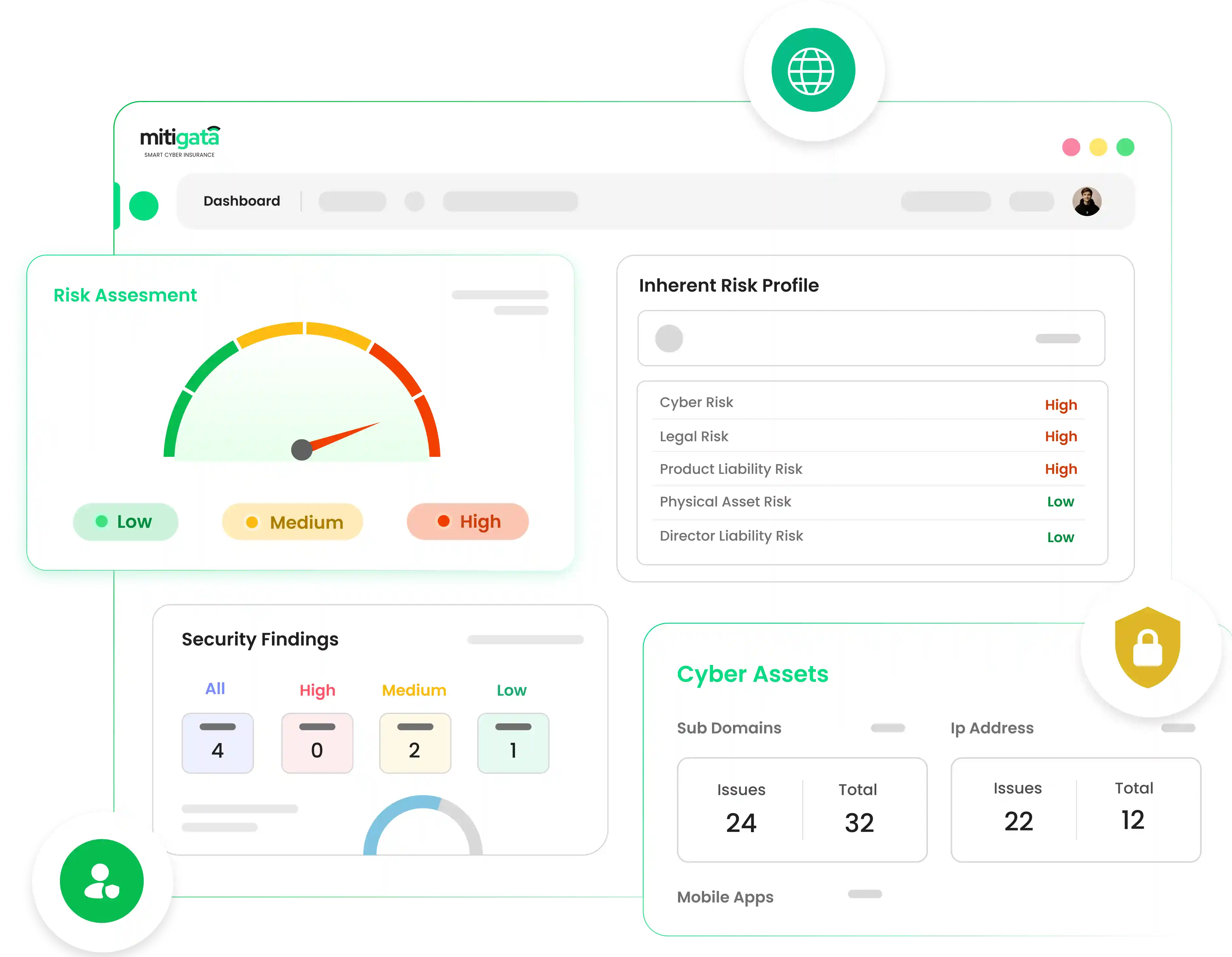
UNDERSTAND THE RISK
Response Processes
Claims & Incident
We've developed a comprehensive approach to claims and incident response processes, aimed at protecting your business from cyber threats.

Our Claims Approach
Mitigata revolutionizes cyber claims with a swift, coordinated approach. Our in-house team ensures rapid responses, aligning with the quick pace of cyber threats. This strategy allows us to minimize your losses and expedite your return to normal operations, safeguarding your business's core values.

Our Incident Response
At Mitigata, our incident response team provides immediate, comprehensive support following a cyber threat. We're equipped to reduce the impact on your operations with our real-time, expert assistance. Experience how our proactive response protects your organization.

Our Broker Advantage
Brokers play a crucial role in navigating cybersecurity and insurance complexities. Mitigata supports you in offering unparalleled coverage and protection through our Active Cyber Insurance, streamlining the process and enhancing client satisfaction.
Things You
Probably Wonder
Cyber insurance acts as a financial safety net, providing coverage against various cyber threats and helping businesses recover from the financial losses incurred due to cyber attacks.
If your business relies on digital assets, handles sensitive data, or operates online, cyber insurance is crucial to protect against potential financial losses and reputational damage resulting from cyber attacks.
In the unfortunate event of a cyber attack,Insurance coverage placed through Mitigata helps mitigate financial losses, facilitates incident response efforts, and supports business continuity to minimise the impact on your operations.
While Mitigata's cyber insurance covers a wide range of cyber threats, there may be exclusions depending on the specific policy terms. It's essential to review your policy carefully and discuss any concerns with your insurance provider.
The cost of cyber insurance varies depending on factors such as the size of your business, industry, coverage limits, and risk profile. However, investing in cyber insurance can be a cost-effective way to mitigate the potentially significant financial consequences of cyber attacks.